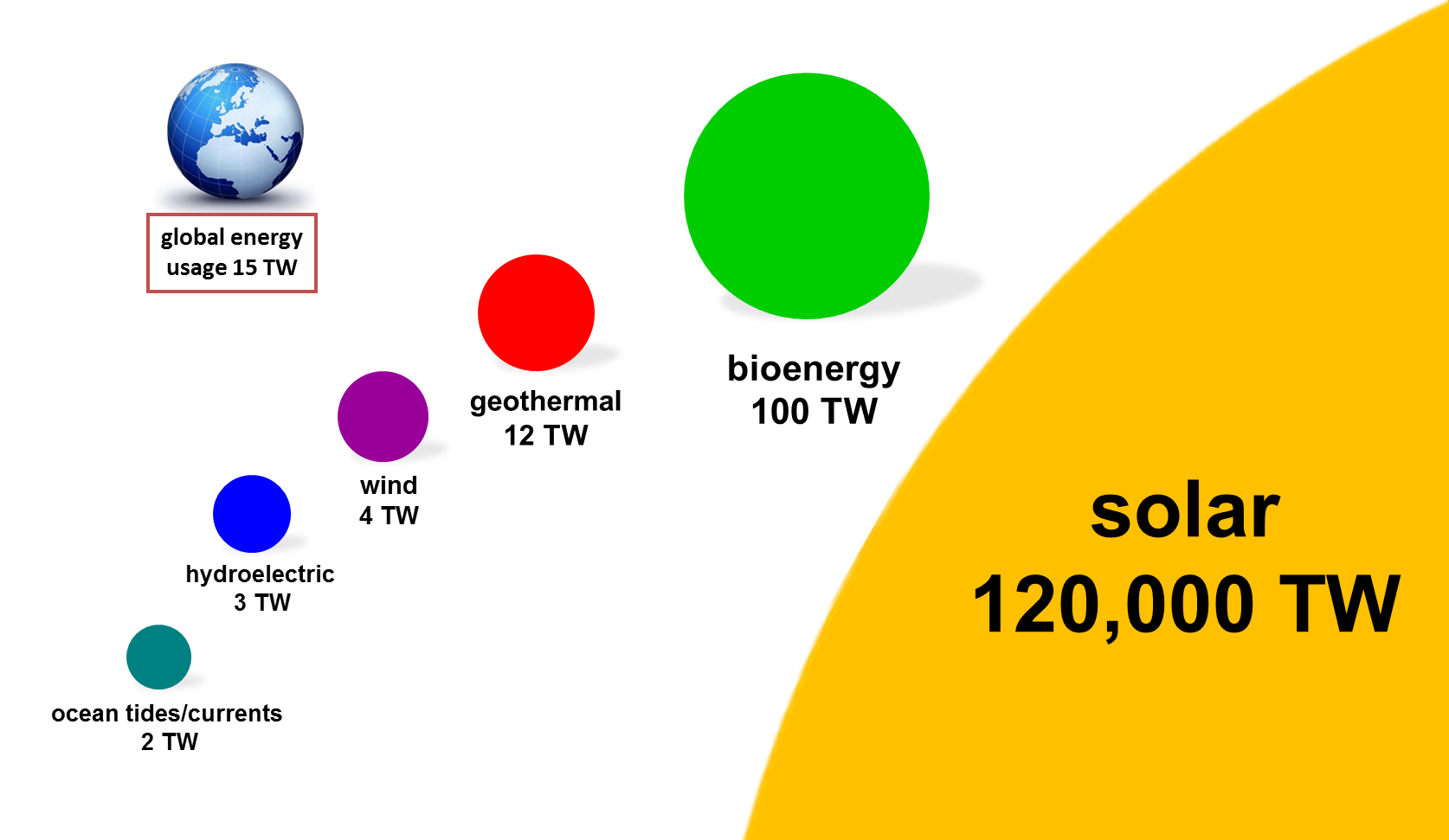
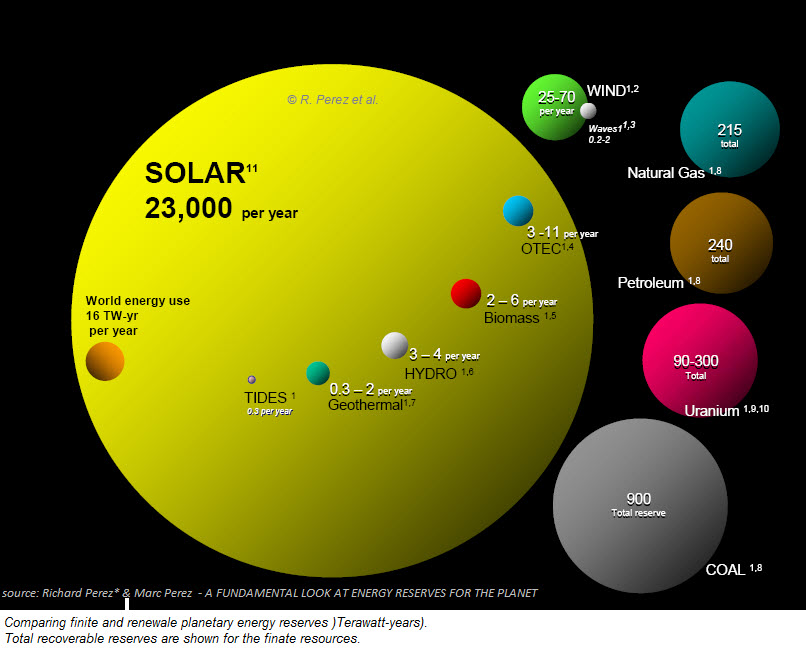
Renewable Energy Sources (RES) are the non-fossil energy sources, namely: wind, solar, geothermal, wave, tidal, hydropower, biomass and biogas, landfill gas and gases from biological treatment facilities (as defined by Directive 2001/77 / EC.)



Renewable Energy Sources (RES) are in abundance in the natural environment and are the first form of energy that man used before turning to the use of fossil fuels.
RES are inexhaustible, for all intends and purposes, in the sense that they are created directly or indirectly by the sun and therefore will disappear when the sun goes out, which is estimated to be in some 5 billion years (https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/sun-age / en /).
Their use does not pollute the environment and their exploitation depends on the existing technological possibilities. For all countries, RES are a domestic source of energy that contribute to their energy balance, reducing their dependence on expensive imported fuels (oil and gas) as well as enhancing the security of energy supply.
At the same time, they contribute to the improvement of the quality of their immediate environment. The energy sector - heavily reliant on the exploitation of fossil fuels - is primarily responsible for environmental and atmospheric pollution, with fossil fuels releasing solid, liquid and gaseous pollutants, since their exploitation activities involve, from mining and transport to storage and combustion.
But above all, RES contribute to tackling climate change caused by the global temperature rise, which is caused by the increase of carbon dioxide concentration (and other greenhouse gases such as methane, water vapor, etc.) in the atmosphere.
Energy activities based on the use of fossil fuels cause two-thirds of the carbon dioxide emissions (http://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/syr/).
Hence, the substitution of fossil fuels with RES is the spearhead in coping with climate change.
The main advantages of RES:
- They are practically inexhaustible sources of energy and therefore lead first to the reduction and subsequently to the elimination of the dependence on conventional energy resources, which, as estimated, will be exhausted during the current century or the next.
- They are indigenous sources of energy and contribute to the enhancement of energy independence and to the security of energy supply at a national level.
- They are geographically dispersed and lead to the decentralization of the energy system, which makes it possible to meet needs at a local and regional level, to reduce the environmental burdens on the central infrastructure systems and to reduce energy transmission losses.
- This geographical dispersion means that all countries have a significant RES potential and therefore no military campaigns are needed to acquire and maintain them, something that is greatly done for oil and gas.
- They allow the choice of the appropriate form of energy according to the needs of the user, leading to the rational use of energy resources.
- They have low operating costs, which now compete with coal.
- RES investments create many jobs at local / regional level.
- They can contribute to the regeneration of national, regional or local economies by delivering a social dividend to local communities forgotten by the metropolis
- They are uniquely friendly for human and the environment, and their exploitation does not damage ecosystems since their use is not associated with solid liquid or gaseous pollutants.
- From an environmental point of view, RES have the least impact on the environment, since there is no development without environmental impact. The characteristics of an Environmental intervention from a RES project are the following:
- It has a local only geographic dimension - with no effect elsewhere.
- It has a point time duration of intervention - it ends with the end of the project.
- The only thing that remains is the subjective, by definition, aesthetic issue/ element.
However, they mostly have a decisive contribution to tackle climate change by replacing fossil fuels which are responsible for 2/3 of greenhouse gases.