Climate Change Is Moving This Restaurant From Italy to Switzerland.
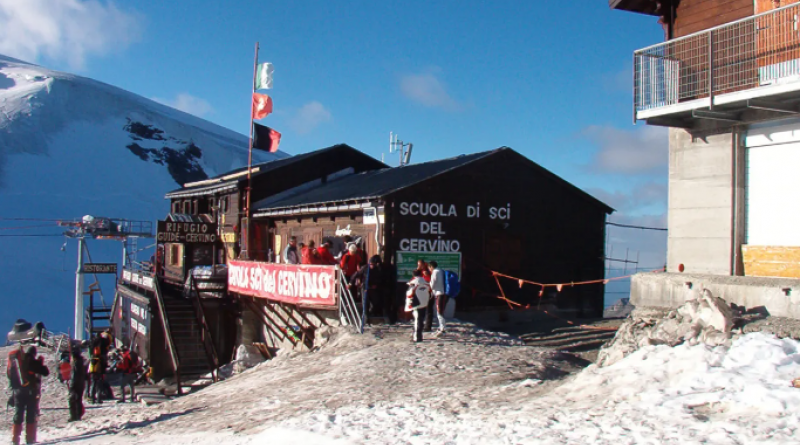

Rifugio Guide del Cervino is a bar and restaurant atop the Plateau Rosa, a glacial ridge in the Italian Alps. Or at least, it was. Climate change is moving it inexorably toward Switzerland as the glacier on which it sits steadily melts.
We're used to news reports about people and wildlife forced to move by the effects of climate change. But in this corner of the Alps, climate change is literally moving the border between Italy and Switzerland.
When the Rifugio was built in 1984, it was on the Italian side of the border. Since then, climate change, accelerated by the 2003 European heatwave which caused Alpine glaciers to lose 10% of their mass, has led to the glacier retreating towards Switzerland.
It could prove to be a headache for restaurateur Lucio Trucco. If the eatery were declared to be in Switzerland, he would have to make some major changes to his kitchens, including installing Swiss power sockets, which his Italian plugs won't fit.
Faced with such issues, Trucco, an experienced mountain guide, says he knows which side of the border his restaurant is located. He has been quoted in media reports as insisting: "The building hasn't moved, so this is still Italy."
Mobile Border
The Rifugio has 40 guest beds and is a popular destination for climbers attempting the Breithorn (4,164 meters, or 13,661 feet), neighbor to the Matterhorn on the Swiss border. But that's as close to Switzerland as Trucco wants his restaurant to get.
For now, COVID-19 restrictions mean the Rifugio is closed. Italy is starting to lift its coronavirus lockdown, but with bars among the businesses allowed to open, some people say social distancing in ski resorts may prove hard to implement.
In 2009, Italy and Switzerland agreed their border should be mobile, shifting to accommodate changes caused by glacial melting. Movements are monitored using GPS sensors allowing the border to be redrawn as the ice moves.
Sea Levels
Climate change is affecting other borders around the world. In the southern U.S., rising sea levels and the canalization of the Mississippi river are the culprits. Since the 1930s, Louisiana has seen more than half a million hectares of its coastal territory disappear under the waves.
As Pulitzer Prize-winning author Elizabeth Kolbert put it in a recent article for the New Yorker: "If Delaware or Rhode Island had lost that much territory, the U.S. would have only forty-nine states. Every hour and a half, Louisiana sheds another football field's worth of land."
Shrinking glaciers are one of the most visible demonstrations of the effects of global warming. The U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says the amount of ice lost since 1980 is equivalent to removing a 24-meter (79-foot) slice off the top of each glacier.
More than one-sixth of the world's population, particularly in China, India and other Asian countries, depend on glaciers for drinking and irrigation water, according to scientists at Columbia University.
Global temperatures are estimated to have risen by at least 1°C (33.8 degrees F) above pre-industrial levels, and experts warn urgent action is needed to curb emissions. A rise above 1.5°C (34.7 degrees F) will cause glaciers in Asia, for example, to shrink by two-thirds by the end of the century.
21 May 2020
EcoWatch