This is what emerging technologies mean for the future of infrastructure.

- The emerging technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution are disrupting traditional infrastructure markets and creating new ones;
- This change coupled with the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic have resulted in increased demand and supply uncertainty;
- New infrastructure will be required and private investment, at higher levels than has been allocated to date, will be needed in order to close a multi-trillion-dollar funding gap.
The transformative and disruptive technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution are reimagining the possibilities for the built environment. Advances in data proliferation, connectivity, automation and sustainability technology are disrupting existing markets and creating new ones altogether in many infrastructure sub-sectors.
The COVID-19 crisis is also causing profound shifts in societal needs and consumer demands, hastening the adoption of certain technologies that threaten to erode the market share of assets that were conventionally highly used. Taken together, these dynamics are now shaking long-held assumptions about the essential and monopolistic nature of some infrastructure services.
As noted in the recent report from Marsh & McLennan Advantage and the Global Infrastructure Investor Association (GIIA), Global Risks for Infrastructure: The Technology Challenge, these two forces have resulted in increased competition for owners and operators of certain assets while reducing or changing demand for others.
Yet the infrastructure sector has historically been slow to understand and adopt new technology. In 2019, the World Economic Forum remarked that it remains “one of the least digitally transformed sectors of the economy”. This disconnect creates the potential for stranded assets – it is estimated that the disruptive power of renewables will strand almost $20 trillion worth of traditional fossil fuel-based energy assets worldwide within the next 30 years. As such, the time is now for the infrastructure sector to sit up and really take notice of the risks that technological disruption entails.
An evolving competitive landscape
Rapid technological developments have often lowered the traditionally high barriers to entry for infrastructure services that had previously been regarded as monopolistic in nature. As new technologies become cheaper or more efficient, opportunistic disruptors increasingly stake a claim for market share in many sub-sectors by offering attractive alternatives to existing products and services. This creates new risks for incumbent investors and raises hard questions about asset valuations and long-term contracting structures.
Technological disruption is particularly relevant to the energy sector, with renewable energy and energy storage technologies making large strides towards cost and efficiency parity with fossil fuel-based electricity generation. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, the cost of utility-scale solar photovoltaic energy fell 82% between 2010 and 2019, while new solar and wind projects are already cheaper than existing coal-fired power plants in many regions and new coal plants in all major markets. Consequently, global coal power capacity has fallen for the first time on record, with more generators being shut down than commissioned in the first half of 2020.
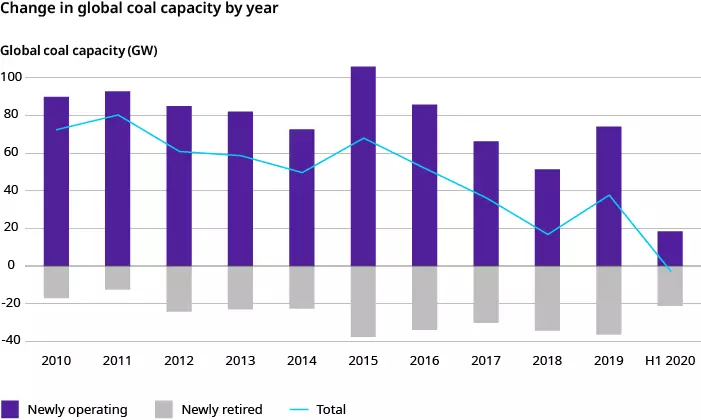
Image: Marsh & McLennan Advantage/Carbon Brief and Global Coal Plant Tracker
Renewable energy has arguably already broken the monopoly of fossil fuel-based electricity generation by providing consumers with a genuine alternative that is moreover backed by the ongoing crusade against climate change. With green technology poised to become more commercially viable at large scales in the coming years (in part driven by the continuation of government-backed subsidies), fossil fuel power may eventually lose the centrality it has long enjoyed in the world’s energy system. Indeed, global energy infrastructure financing is already moving away from fossil fuel-based assets and toward renewables with investment in the latter expected to overtake downstream oil and gas investment in the near future.
The rise of renewables is even threatening to strand assets in other infrastructure sub-sectors, such as freight rail tracks that exclusively transport coal to power plants. As the Fourth Industrial Revolution rolls on, the competitive pressure from emerging technologies will only continue to transform the outlook for incumbent infrastructure investors and operators.
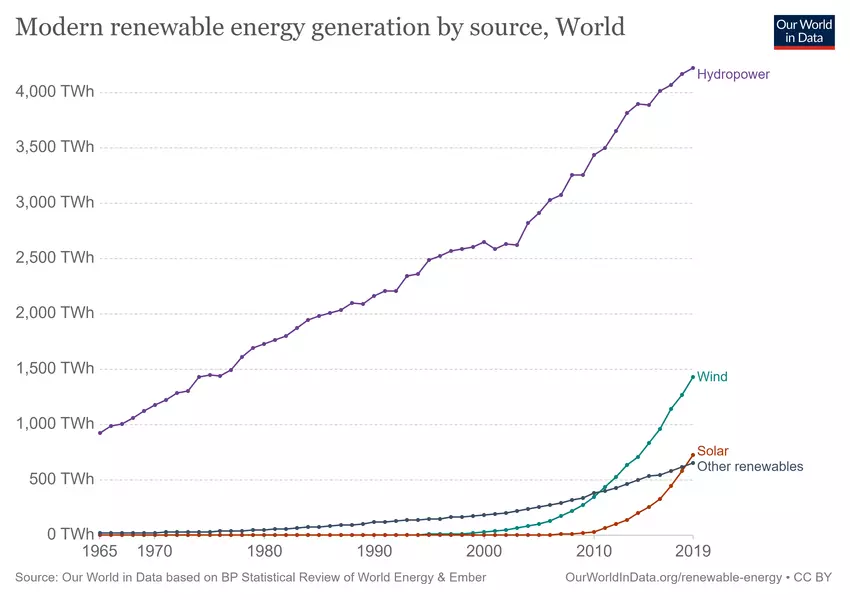
Image: Our World in Data
Reduced utilization rates for transportation assets
The societal fallout from the COVID-19 crisis is also expediting a shift in customer needs and preferences which can further undermine the fundamental and essential nature of assets and services.
For instance, the downturn in traffic for commuter rail and international air travel has been matched by the rapid adoption of remote working technologies and shifting work practices. Data from the US Bureau of Transportation Statistics suggests that, since the COVID-19 lockdowns began, more people stayed home in any given week of 2020 than in the corresponding week in 2019. The dramatic transformation in mobility patterns has induced seismic shockwaves across various transportation sub-sectors. US monthly urban rail utilization is down to almost a quarter of 2019 levels; total monthly air travel is down 65% year-on-year.
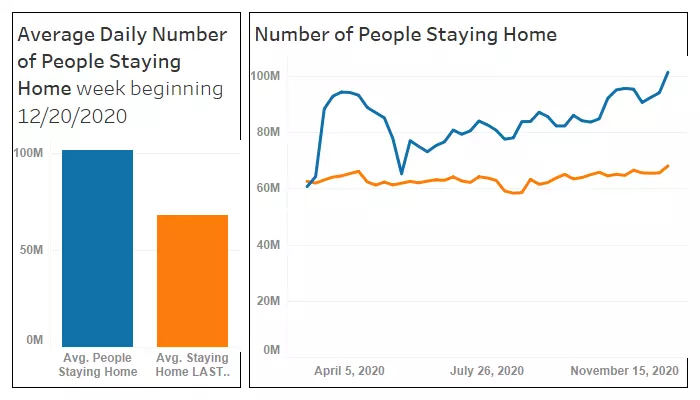
Image: Bureau of Transportation Statistics




